Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration's Strategic Prevention Framework
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration's (SAMHSA) Strategic Prevention Framework (SPF) is a systemic community-based approach, which aims to ensure that substance abuse prevention programs can and do produce results.
The idea behind SPF is to use the findings from public health research along with evidence-based prevention programs to build capacity within States and the prevention field. This in turn will promote resilience and decrease risk factors in individuals, families, and communities.
Community Prevention and Wellness Initiative Planning Framework
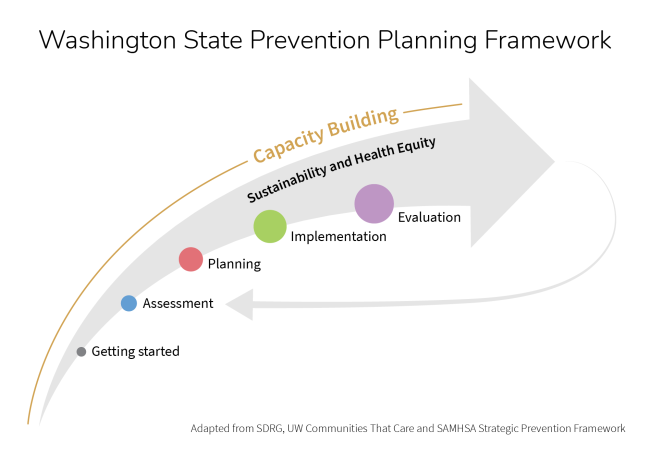
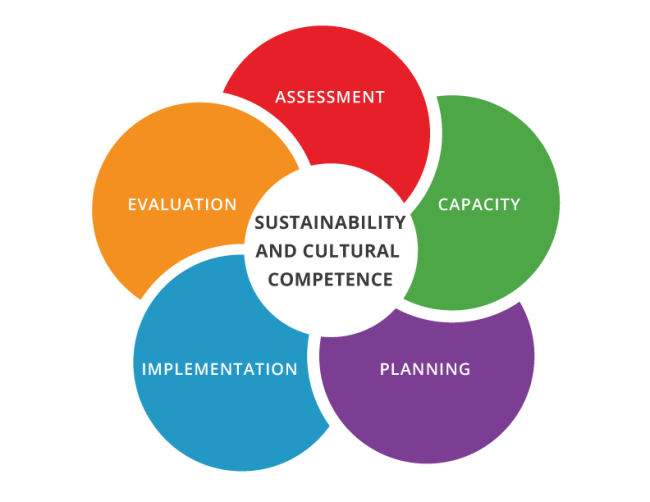
The Division of Behavioral Health and Recovery (DBHR) Community Prevention & Wellness Initiative (CPWI) uses the SPF for planning, with two enhancements: a “Getting Started” section and an expectation that “Capacity Building” is ongoing throughout the process. All tasks associated with CPWI planning must be conducted in a culturally competent manner, and include sustainability planning and implementation.
Assessment
The assessment phase helps define the problem or the issue that a project needs to tackle. This phase involves the collection of data to:
- Understand a population's needs
- Review the resources that are required and available
- Identify the readiness of the community to address prevention needs and service gaps.
To gather the necessary data, States and communities will create an epidemiological workgroup. The data gathered from this workgroup is vital because it will greatly influence a program's strategic plan and funding decisions.
Capacity Building
Capacity building involves mobilizing human, organizational, and financial resources to meet project goals. Training and education to promote readiness are also critical aspects of building capacity.
Planning
Planning involves the creation of a comprehensive plan with goals, objectives, and strategies aimed at meeting the substance abuse prevention needs of the community. During this phase, organizations select logic models and evidence-based policies and programs. They also determine costs and resources needed for effective implementation.
Implementation
The implementation phase of the SPF process is focused on carrying out the various components of the prevention plan, as well as identifying and overcoming any potential barriers. During program implementation, organizations detail the evidence-based policies and practices that need to be undertaken, develop specific timelines, and decide on ongoing program evaluation needs.
Evaluation
Evaluation helps organizations recognize what they have done well and what areas need improvement. The process of evaluation involves measuring the impact of programs and practices to understand their effectiveness and any need for change. Evaluation efforts therefore greatly influence the future planning of a program. It can also impact sustainability, because evaluation can show sponsors that resources are being used wisely.
Sustainability
Sustainability refers to the process through which a prevention system becomes a norm and is integrated into ongoing operations. Sustainability is vital to ensuring that prevention values and processes are firmly established, that partnerships are strengthened, and that financial and other resources are secured over the long term.
Cultural Competence
Cultural competence is the process of communicating with audiences from diverse geographic, ethnic, racial, cultural, economic, social, and linguistic backgrounds. Becoming culturally competent is a dynamic process that requires cultural knowledge and skill development at all service levels, including policymaking, administration, and practice.